Furan test
To analyze and determine the polymerization degree (PD) of paper insulation, a direct evaluation method can be used. This requires taking out a few strips of insulation paper, weighing about 2g, from inside the transformer. The amount of paper required is not large, but this is an intrusive test. To take a sample, the machine must be stopped and part of the insulation of the machine is destroyed during the sampling process, and therefore is often dangerous for the transformer itself. Furan analysis is an alternative method.

Paper is the main insulating material used in oil transformers. Paper is used in the form of sheets, plates, tapes, and other pressed materials. During the operation of the transformer, the paper is affected by electrical stress, mechanical force in normal operation, and especially when overload and short circuit occur. To ensure the insulating function in the machine, in addition to the insulation requirements, the paper must also have sufficient mechanical strength. The mechanical strength of paper decreases sharply when damp, so drying the machine and filtering the insulating oil in the machine are commonly applied measures to reduce humidity and thereby increase the durability of the insulating paper (in addition to other insulating benefits). However, humidity is not the only problem with insulating paper.
Over time, the cellulose-based insulation inside the transformer gradually degrades. Heat, moisture, and oxygen, as well as oil degradation products, all adversely affect the life of the paper. Each cellulose fiber in paper consists of a bundle of cellulose molecules of varying lengths, located side by side. These molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds between hydroxyl (-OH) groups in their structure. Cellulose molecules are linear polymers made up of a chain of glucose units linked together by glycosidic bonds. As paper ages, the glycosidic bonds break, and the molecule shortens (See Figure 1). As a result, the paper loses its mechanical strength, and the useful life of the transformer is shortened.
A test that can be used to assess the condition of the cellulose inside a transformer is to determine the average degree of polymerization (DP). To assess the aging of the insulation paper in a power transformer that has been in service for a long time, a paper sample can be analyzed to determine the degree of polymerization. New Kraft paper usually has a degree of polymerization in the range of 1,100 to 1,500. A DP of about 150 is also when the paper reaches the end of its useful life.
To analyze and determine the polymerization degree (PD) of paper insulation, a direct assessment method can be used. This requires taking out from inside the transformer a few strips of insulation paper, weighing about 2 g. The amount of paper required is not large, but this is an intrusive test. To take a sample, the machine must be stopped and part of the insulation of the machine is destroyed during the sampling process, and therefore is often dangerous for the transformer itself.
Furan analysis is an alternative method.
Furan derivatives
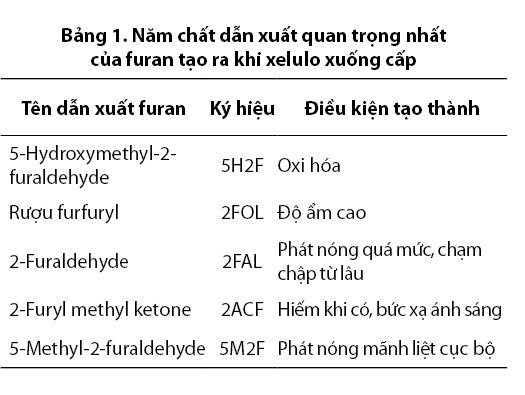
The process of depolymerization of cellulose molecules, i.e., breaking them into shorter segments or into ring structures, produces a number of products that are derivatives of compounds called furans. Furans are five-membered rings consisting of four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, each carbon atom attached to a hydrogen atom. The molecular formula of furan is C4H4O. The five most important furan derivatives that are produced when cellulose degrades, and are soluble in oil to some extent, are listed in Table 1.
Testing procedure
The procedure for the quantitative determination of furan derivatives in insulating oils is detailed in ASTM D 5837, and is briefly introduced here. The oil sample is extracted with another liquid, such as acetonitrile, or by means of a solid phase extraction (SPE). The sample is then analyzed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). The five compounds are separated into a suitable column, each detected by an ultraviolet detector automatically calibrated to the appropriate wavelength. Standard solutions are used for each component required for analysis, which are used to calibrate the instrument. From the data on the standard solutions, the refractive index of each component can be calculated and corrections made accordingly. The results are usually reported in parts per billion (ppb).
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Meaning
The five furans commonly analyzed by this procedure are aromatic (cyclic) compounds that are produced by the degradation of cellulosic materials within the transformer due to normal aging or possibly internal faults. The amount of these products in the transformer oil can therefore be a good indicator of the condition of the cellulosic insulation. To date, normal and limit values have not been established for individual components or for combinations of components. There have been several research programs to determine whether there are any useful relationships that can be used, but so far only the benefit of monitoring trends rather than absolute values in the oil has been established.
If a reliable relationship between the average degree of polymerization and the concentration of individual furan compounds or combinations of furan compounds can be determined, this relationship would have several advantages in assessing the condition of cellulose insulation inside machines. First, it is a non-invasive test procedure. Second, it does not require the machine to be shut down. Third, this laboratory test is less time-consuming and highly sensitive. Efforts are currently being made in this direction.
Paper insulation analysis
When degraded, paper loses tensile strength and produces furan derivatives.
Early detection of paper deterioration can prevent major damage or failure. Dissolved gas analysis in oil was previously the only non-invasive test performed on transformers that could potentially indicate troublesome internal problems. Monitoring CO and CO2 in the oil can provide some insight into the condition of the insulation.
The main objective of the furan test is to determine whether the paper in the transformer is affected by heat. Heat-induced furan is formed in two ways: One is when the paper is damaged by high temperature local heating; the other is under the general heating condition of the transformer and the entire insulation system is heated.
Furan analysis can detect thermal, oxidative and hydrolytic deterioration of insulation. Combining this test with dissolved gas analysis provides a comprehensive picture of the transformer condition. Furan testing should be included in annual maintenance and trend monitoring to monitor insulation condition.
Example of Furan analysis
Case 1
750 kVA, 6.6/0.38 kV transformer
Testing showed a furan content of 10.56 ppm (parts per million), which corresponds to the end of life. It was recommended to check the paper insulation. One month later, the transformer failed. The oil tank ruptured. The initial cause was insulation failure.
Case 2
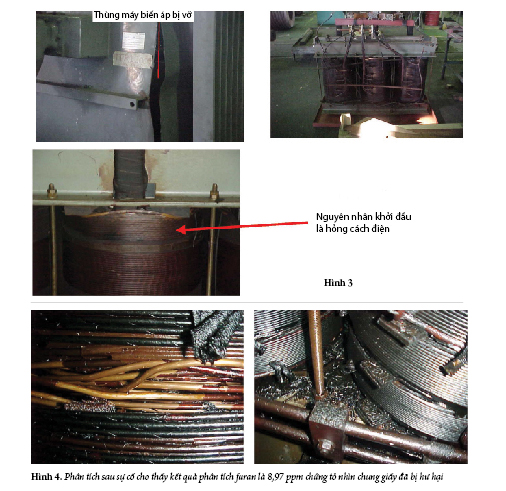
The transformer failed while in operation; the machine was being dehumidified (December 3, 2000).
Post-incident analysis showed a furan content of 8.97 ppm, indicating severe paper damage. The furan generation rate was 160 ppb/month (160 parts per billion/month). According to Morgan Schafer, a furan generation rate of 25 ppb/month is a cause for concern.
From 1995 to December 2005, the machine underwent 10 oil filtrations to remove moisture from the transformer oil and improve the dielectric. Oil filtration did not improve the oil condition.
Dissolved gas analysis showed partial discharges at low energy densities. A CO2/CO ratio of 16.5 indicated deterioration of the insulation paper. Normally, this ratio should be between 3 and 11.
Oil filtration is of no benefit once the solid insulation (paper) has been damaged. In this particular case, it would have been necessary to take the machine into a workshop and re-insulate it.

Conclude
Furan analysis in oil is a cost-effective measure in maintenance planning. Furan analysis data should be considered in conjunction with dissolved gas analysis, liquid insulation testing, and previous maintenance records.
Once a transformer has reached the end of its useful life and is no longer reliable, the only solution is to take it out of service and rewire the windings.
Oil Analysis Laboratory
Best Regards.,
Mr. Nguyen Huu Nhat – Director, Analytical Instruments
Viet Instruments Joint Stock Company
Office: 187 Road No 10, Ward 8, Go Vap Dist, Ho Chi Minh,Vietnam
T: +84.375136242 | F : +84.8.35107658 | M: +84.909470840 – 0901427775
E-mail: nhat.nguyen@vietinstrument.com
Website: www.vietinstrument.com
